Poor circulation problems usually develop as you age because your body begins to experience changes, with some more noticeable than others.
A decline in blood circulation poses hidden dangers that could impact your overall health and well-being. Furthermore, you may face dire consequences if these are left unaddressed.
This article looks at the lesser-known risks of declining blood circulation in seniors.
So, whether you are someone who is concerned about your own aging body, or looking out for the well-being of a loved one, this article will provide you with knowledge and tools you need to take charge of your wellbeing.
The Connection Between Age and Circulation Issues
While the human body is an intricate and complex system, there are certain changes that occur as you age, and these changes can have a significant impact on blood flow and overall circulation.

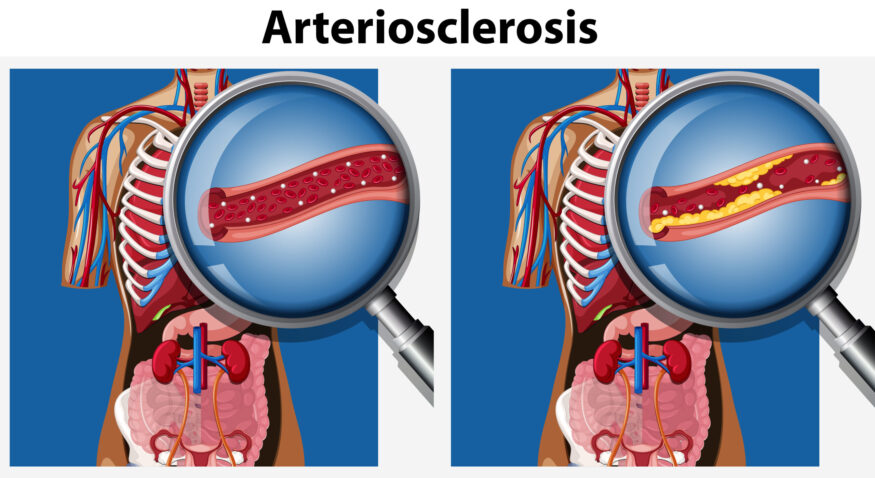
As you grow older, blood vessels naturally become less flexible and may develop plaque buildup, leading to a condition known as arteriosclerosis. Many are already familiar with this condition, but, there are several other changes.
The narrowing of the arteries hinders the smooth flow of blood throughout the body, reducing the delivery of essential oxygen and nutrients to our organs and tissues.
Aging can also lead to a decrease in the production of nitric oxide, which helps relax and widen blood vessels, promoting healthy blood circulation.
Without adequate amounts of nitric oxide, your blood vessels may become constricted, further impairing the flow of blood.
Another age-related change is the weakening of the heart muscle which may slow down the heart rate thereby affecting the efficiency of pumping blood to the rest of the body.
This diminished cardiac function can result in decreased blood supply to vital organs, thereby causing a range of health issues.
What are Your Risks?
Poor circulation in seniors can lead to several serious health risks. It can cause peripheral artery disease (PAD), increasing the risk of heart attack and stroke due to reduced blood flow.
Poor circulation may also result in chronic wounds, particularly in the legs and feet, that heal slowly and can become infected, sometimes leading to amputation.
Reduced blood flow can cause numbness, tingling, and pain, affecting mobility and quality of life. Furthermore, it can lead to deep vein thrombosis (DVT), where blood clots form in deep veins, potentially causing life-threatening complications if they travel to the lungs.
Finally, poor circulation can contribute to cognitive decline and increase the risk of dementia due to insufficient blood flow to the brain. These health risks are discussed in the sections below.
Lifestyle
Lifestyle factors significantly contribute to the risks of poor circulation in seniors. A sedentary lifestyle can lead to obesity and reduced muscle activity, impairing blood flow. Smoking damages blood vessels and increases plaque buildup, further restricting circulation.
Poor diet, high in saturated fats and low in essential nutrients, can lead to arterial blockages and elevated cholesterol levels. Lack of regular physical activity contributes to hypertension and diabetes, both of which exacerbate circulatory issues.
Stress and excessive alcohol consumption can also negatively impact cardiovascular health and diabetes, increasing the risk of poor circulation and associated complications
Cardiovascular Risks of Poor Circulation Problems in Seniors
As we age, our blood vessels naturally undergo changes that can lead to reduced blood flow throughout the body – The Causes of Poor Blood Circulation in Aging Adults.
This poor blood circulation could be related to arteriosclerosis, increased rigidity of the arteries, weakened heart muscles, chronic blood pressure, accumulation of calcium deposits, and impairment of the blood vessel lining.
All can have far-reaching consequences and significantly impact a seniors’ overall health and well-being.
Increased Risk of Cardiovascular Diseases
One of the primary risks associated with poor blood circulation in seniors is an increased likelihood of developing cardiovascular diseases such as heart attacks and strokes.
Without adequate blood flow, the heart has to work harder to pump oxygenated blood to different organs and tissues, increasing the strain on this vital organ.
Over time, this can lead to the development of heart conditions and a higher risk of experiencing a cardiovascular event.
Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD)
Furthermore, inadequate blood flow can contribute to the development of peripheral artery disease in seniors.
PAD occurs when plaque (arteriosclerosis) builds up in the arteries that supply blood to the legs and other extremities.
No wonder many seniors complain about poor circulation in the legs. This can cause pain, cramping, and reduced mobility, making it challenging for seniors to engage in physical activities and maintain an active lifestyle.
Decline in Cognitive Function Due to Circulation Issues
In addition to cardiovascular issues, poor blood circulation seniors can impact cognitive function. The brain needs a steady supply of oxygen and nutrients through the bloodstream to function optimally.
Reduced blood flow can compromise brain health, leading to cognitive decline and an increased risk of developing conditions such as dementia or Alzheimer’s disease.
Because the brain relies on a steady supply of oxygen and nutrients through the bloodstream, when blood flow to the brain is compromised, cognitive function may be affected.
This may cause issues such as memory loss, confusion, and difficulty with problem-solving. Consequently, seniors with poor blood circulation are at a higher risk of developing age-related cognitive decline.
This highlights the importance of addressing circulation issues to help maintain brain health.
Slower Wound Healing and Increased Susceptibility to Infections
Seniors with blood circulation issues may experience slower wound healing and experience an increased susceptibility to infections.
Proper blood flow is necessary to transport immune cells and nutrients to all parts of the body that need healing. When blood circulation is compromised, wounds may take longer to heal and seniors may be more prone to infections, which can be challenging to manage and treat in older individuals.
Understanding the risks and complications associated with poor blood circulation issues in seniors is necessary to properly implement preventive measures.
Consequently, seniors with blood circulation problems may experience a range of age-related health issues that can significantly impact their overall well-being.
Lifestyle Contributing Factors
Smoking and Diet: Long-term smoking and unhealthy dietary habits can accelerate the development of atherosclerosis and worsen blood circulation.
Unfortunately there are many older adults with these unhealthy habits which can contribute to poor circulation problems.
Medications and Health Conditions: Certain medications and health conditions, more prevalent in older adults, can have side effects or complications that cause blood circulation problems such as PAD, diabetes, atherosclerosis, high blood pressure and more.
For example, some medications may lower blood pressure to levels that restrict circulation and cause issues .
Decreased Physical Activity: Many seniors become less physically active over time, which can also contribute to obesity and poor circulation. Regular physical activity helps improve blood flow by promoting the dilation of blood vessels and enhancing the pumping action of the heart.
Strategies to Improve Blood Circulation and Enhance Vitality
Regular Exercise
One of the most effective ways to improve blood circulation is through regular exercise. Engaging in physical activity helps to strengthen the heart and increase its efficiency in pumping blood around the body.
Find an exercise routine that suits your abilities and preferences. This can range from brisk walks, swimming, or participating in low-impact exercises like yoga or tai chi.
Incorporating exercise into your daily routine can stimulate blood flow, lower the risk of cardiovascular disease, and maintain overall health.
Healthy Diet
Maintaining a healthy diet also plays a vital role in improving blood circulation. Foods rich in antioxidants, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, help to reduce inflammation and promote healthy blood vessels.
Also consuming foods high in omega-3 fatty acids, such as fatty fish, walnuts, and flaxseeds, can help to improve blood flow by reducing the risk of blood clot formation.
You should try to limit intake of processed and fatty foods, as these can contribute to arterial plaque buildup and cause blood circulation issues.
Stress Level Management and Poor Blood Circulation
Managing stress levels is important to improve blood circulation. Stress can have a detrimental effect on the cardiovascular system, causing blood vessels to constrict and impair blood flow.
You can combat stress by engaging in relaxation techniques such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, or practice mindfulness or the use of essential oils.
A novel way to get rid of stress : Check out the Tibetan Singing Bowl Set – Easy to Play – Creates Beautiful Sound for Holistic Healing, Stress Relief, Meditation & Relaxation.
Make time for hobbies, spend time with loved ones, and seek support from a therapist or support group to also help reduce stress and improve blood circulation.
Prescribed Treatments
In addition to these lifestyle changes, you should follow any treatments prescribed to address circulation issues. This may include taking medication to manage conditions like high blood pressure or high cholesterol, or undergoing therapies such as physical therapy to promote blood flow.
By working closely with your healthcare professionals and sticking to prescribed treatments, you can effectively manage circulation issues and reduce the risk of developing serious health problems.
By implementing these strategies to improve blood circulation and enhance overall vitality, seniors can reduce their risk of age-related health issues.
Best Preventive and Management Products for Poor Circulation Problems
Poor circulation in aging adults can lead to issues like cold extremities, numbness, swelling, and even serious conditions like varicose veins or deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
There are several preventive and management products available on the market that can help to help improve circulation.
Preventive Products:
- Compression Socks or Stockings – Help prevent blood pooling in the legs, reduce swelling, and improve circulation.
- Leg Elevation Pillows – Elevating the legs promotes better blood flow and reduces strain on veins.
- Foot Massagers & Circulation Boosters – Devices like vibration massagers or EMS (electrical muscle stimulation) can stimulate circulation in the legs and feet.
- Anti-Fatigue Mats – Useful for seniors who stand for long periods to reduce strain on the legs.
- Hydration & Electrolyte Supplements – Staying hydrated helps maintain blood viscosity and circulation.
Management Products:
- Blood Circulation Supplements – Omega-3 fatty acids, CoQ10, L-arginine, and ginkgo biloba support healthy circulation.
- Infrared Heating Pads – Improve blood flow and relieve muscle stiffness.
- Ankle and Foot Braces – Provide support for those with mobility issues or swelling.
- Adjustable Recliners with Leg Support – Elevates legs to prevent fluid buildup and improve circulation.
- Exercise Equipment – Seated pedal exercisers or mini treadmills keep the legs moving without high-impact strain.
Conclusion – Poor Circulation Problems
Poor circulation in seniors is a matter that should never be taken lightly. This is because of the real dangers posed – cardiovascular diseases, decline in cognitive function, and slower wound healing and susceptibility to infections.
Now that you know the facts, what is your next step? Engage in preventative measures with appropriate lifestyle changes before the onset of symptoms. Promptly consult your healthcare provider if you notice any symptoms related to circulation issues.
Leave a comment to let us know of your challenges with poor circulation in the extremeties.
Related Articles for Additional Reading
- Foot Problems and Diabetes. Why Important for Seniors?
- The Causes of Poor Blood Circulation in Aging Adults
- Compression Leg Socks – How to Buy and Select
- The Best Products that Can Help Improve Poor Blood Circulation
- How to Select and Buy Womens Compression Socks
- Compression Socks For Men or Women – Better than Unisex?
FAQ for Poor Circulation Problems in Seniors
What are the signs of blood circulation problems?
Common signs include cold extremities, swelling, fatigue, muscle cramps, and slow healing of wounds.
What causes poor circulation in legs?
Causes include arterial blockages, blood clots, diabetes, obesity, and smoking. A sedentary lifestyle and certain medical conditions such as peripheral artery disease (PAD) can also contribute.
How are circulation issues in the legs treated?
Improving and treating leg circulation can be achieved through lifestyle changes regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding prolonged sitting or standing, and wearing compression socks and stockings. Regular exercise and a healthy diet can also help.
Other treatment options include lifestyle changes, medications, and, in severe cases, surgical interventions.
What are the symptoms of poor circulation in legs?
Symptoms include pain, cramping, swelling, numbness, and a tingling sensation in the legs, especially during activity.
References
Merck’s Manual. Heart Attack https://www.merckmanuals.com/home/quick-facts-heart-and-blood-vessel-disorders/coronary-artery-disease/heart-attack?query=circulation%20problems